There are many dental terms that are difficult for patients to understand, and while “Dentist” is associated with a doctor who treats teeth, a narrow specialization like “Periodontics” raises many questions for our patients. So let’s figure it out: “What is periodontics and a periodontist?”.
What is Periodontics?
Periodontics is a branch of dentistry that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the supporting structures of the teeth (gums). The periodontium includes all the tissues located around the tooth – the gums, the bone in which the root of the tooth is located, and the ligaments of the tooth. The most common diseases in periodontics are gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontosis.
What are periodontal diseases?

Gingivitis is a superficial inflammation of the gums. It is divided into catarrhal, hypertrophic, and ulcerative. Catarrhal gingivitis occurs with redness and swelling of the gums, often accompanied by bleeding. Hypertrophic gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the size of the gums. Ulcerative gingivitis involves the formation of ulcers on the gums and their death (necrosis).
Periodontitis is one of the most common diseases in dentistry today. It is a disease in which there is inflammation of the gums and surrounding tissues. The seriousness of this disease lies in the fact that tooth loss, sometimes even healthy teeth, is possible when the inflammation spreads to the bone surrounding the tooth.
Today, one in two patients suffers from periodontal diseases.
Periodontitis is divided into three degrees of severity: mild, moderate, and severe. In the mild stage, patients experience bad breath, itchy gums, and the appearance of slit-like spaces between the tooth and gum, called periodontal pockets. In the moderate stage, severe pain appears in the affected teeth and gums, the pockets between the tooth and gum deepen, and bone pockets appear. In this stage of the pathological process, the patient’s general condition worsens, and severe intoxication of the body (chronic sepsis) can develop.
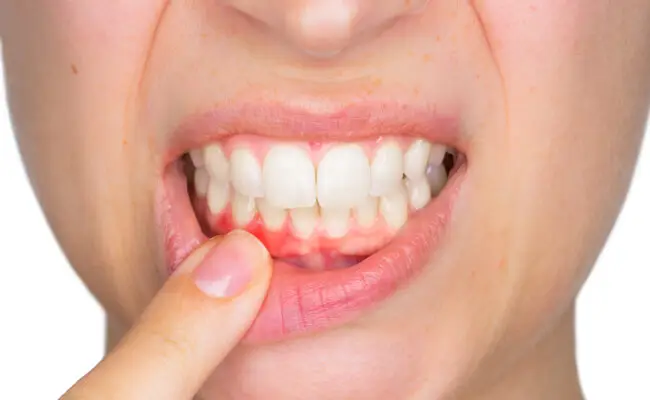

In severe cases of the disease, the teeth become very loose, which can lead to their complete loss. Causes of this disease can be malocclusion, dental calculus, and poor-quality dental prosthetics.
The success of therapy largely depends on timely treatment by a specialist at the first appearance of symptoms such as bad breath, bleeding, swollen gums, dark plaque on the teeth, and dental calculus.
What does a periodontist do?
Periodontists are narrowly specialized doctors who treat and prevent gum diseases. A periodontist has a range of modern theoretical knowledge that, in practice, leads to positive treatment outcomes. The condition of the patient’s oral cavity and overall health depends on the professionalism of such doctors. After all, neglected gum diseases often lead to the penetration of pus into the blood, inflammatory processes, and the inability to chew food normally, which affects the entire body as a whole, since all organs are interconnected, and the failure of one system leads to the failure of the whole organism. In such cases, a regular dental therapist will not help.
Are periodontal diseases treatable?
Patients often ask: “Is it possible to completely cure periodontitis, and what is the guarantee of oral health improvement?” Today, modern dentistry allows us to improve the quality of diagnosis (specific tests and x-ray diagnostics), treatment, and prevention of periodontal tissue diseases, which includes comprehensive treatment with an individual approach to each patient.
One of the modern methods of gum treatment is plasmolifting, which, in combination with complex treatment, leads to lasting results. A beautiful smile is not only pearly white teeth but also healthy gums, the health of which allows you to perform one of the most important functions of teeth – chewing.
What is Plasmolifting?

Dent VIP clinic, Chisinau, Moldova
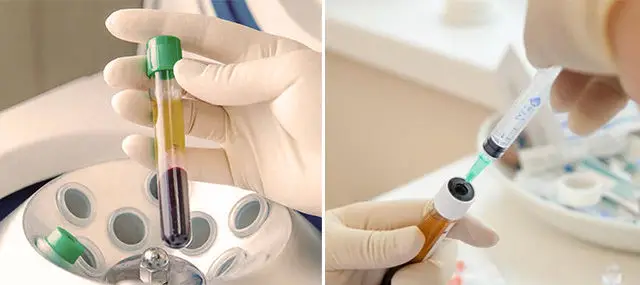
It is a unique tissue regeneration method using plasma obtained from the patient’s own blood, enriched with platelets and growth factors. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates the regeneration of periodontal tissues, relieves bleeding and inflammation of the gums, strengthens and nourishes the gums, thus prolonging the remission phase (stabilization of the process) and reducing the frequency of exacerbations, thereby improving the patient’s quality of life.
How is the Plasmolifting Procedure Performed?
- Before the plasmolifting procedure, it is necessary to perform ultrasonic removal of dental calculus followed by polishing the tooth surface with the “Air Flow” system. (The plasmolifting procedure can be performed on the same day or the next day after cleaning)
- Blood sampling
- Plasma injection into the gums is performed after anesthesia.
What effect is achieved after the plasmolifting procedure?
- Reduces gum inflammation.
- Eliminates bleeding.
- Relieves pain (analgesic effect)
- Reduces tooth mobility.
- Gums acquire a physiological color (pale pink)
- Eliminates bad breath.
- Stops the progression of periodontal disease.
- Improves implant integration.
- Reduces the risk of implant rejection.
- Accelerates healing of the socket area after tooth extraction.
- Shortens the rehabilitation period after maxillofacial surgery.
- Also used as a preventative measure for periodontal disease.
- Improves hemodynamics (blood supply to the gums)
- Activates metabolism in cells.
- Enhances nutrition and oxygen exchange in periodontal tissues.
- Improves local immunity.
Contraindications
- Elevated body temperature at the time of the procedure
- Blood diseases
- Viral infections, including viral hepatitis B, C (except hepatitis A)
- Oncological diseases
The unique, modern method of plasmolifting, combined with complex treatment of gum diseases, guarantees an improvement in the patient’s condition, thereby improving the health and quality of life of our patients, taking into account visits to the periodontist every six months. Your dazzling smile is not only healthy teeth, but also your healthy gums!


